Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and play a crucial role in various biological processes. Their unique structures and properties dictate how they interact within the body and with other molecules. One central aspect of amino acids is their polarity, which significantly influences their behavior in different environments, particularly in aqueous solutions. In this article, we will delve into the question of whether amino acids are polar, exploring the implications of their polarity on their function and interactions.
Understanding the polarity of amino acids is essential for anyone studying biochemistry, molecular biology, or related fields. Polarity affects how amino acids behave in physiological conditions, influencing protein folding, enzyme activity, and cellular signaling pathways. By examining the characteristics that determine the polarity of amino acids, we can gain insight into their diverse roles in living organisms.
As we navigate the complexities of amino acid polarity, we will address common questions surrounding this topic. We will explore the definitions of polar and nonpolar amino acids, the factors that contribute to their polarity, and the significance of these properties in biological systems. Join us as we uncover the intricate relationship between amino acids and polarity, shedding light on their importance in the realm of life sciences.
What Are Amino Acids and Their Importance?
Amino acids are organic compounds that serve as the fundamental building blocks of proteins. They contain an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a distinctive side chain that determines their unique properties. There are 20 standard amino acids, each playing specific roles in biological processes. These amino acids link together via peptide bonds to form polypeptides, which subsequently fold into functional proteins.
How Do Amino Acids Contribute to Protein Structure?
The structure of proteins is intricately linked to the properties of their constituent amino acids. The sequence and composition of amino acids determine how a protein folds, which ultimately affects its functionality. The interactions between amino acids—such as hydrogen bonding, ionic interactions, and hydrophobic forces—are influenced by their polarity. Understanding these relationships is crucial for unraveling the complexities of protein structure and function.
Are All Amino Acids Polar?
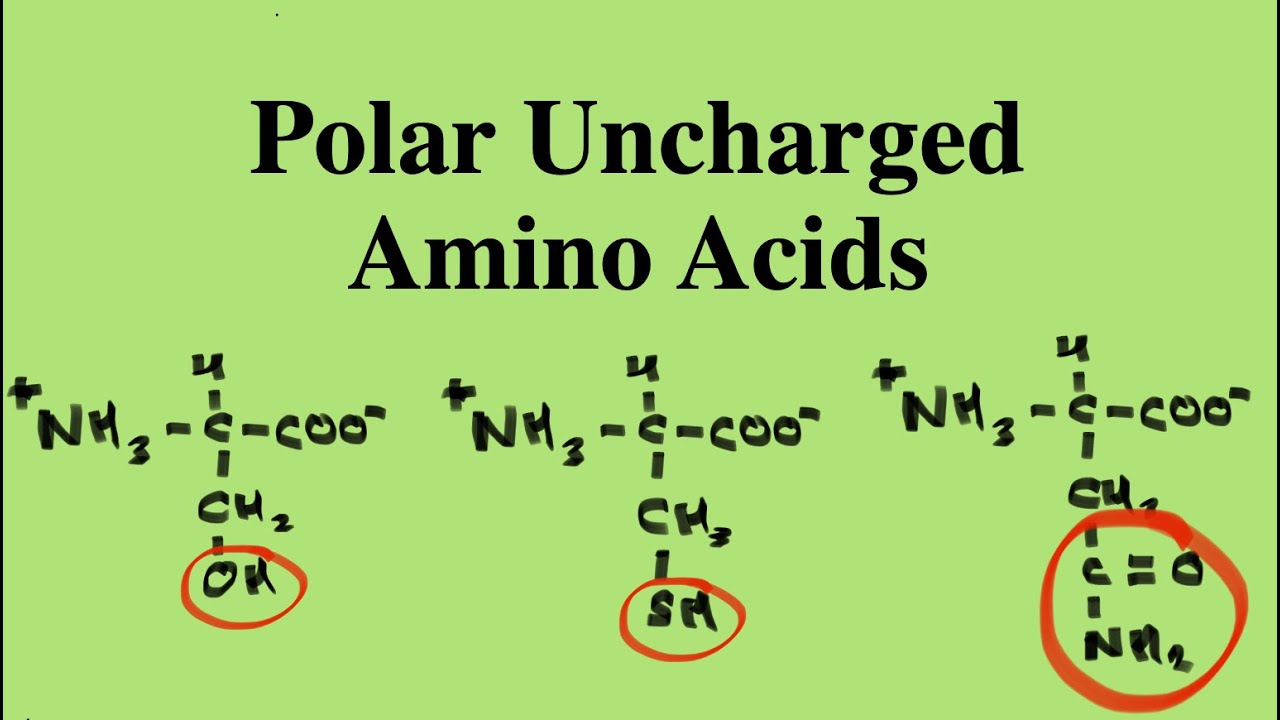
No, not all amino acids are polar. Amino acids can be broadly classified into two categories based on their side chains: polar and nonpolar amino acids. Polar amino acids have side chains that contain electronegative atoms, such as oxygen or nitrogen, which can form hydrogen bonds with water and other polar molecules. Nonpolar amino acids, on the other hand, have side chains composed primarily of carbon and hydrogen, making them hydrophobic and less likely to interact with water.
What Factors Determine the Polarity of Amino Acids?
The polarity of amino acids is influenced by several factors, including:
- Side Chain Composition: The presence of electronegative elements in the side chain increases polarity.
- Hydrogen Bonding: Ability to form hydrogen bonds with water enhances polarity.
- Electronegativity: Atoms with higher electronegativity contribute to polar characteristics.
- Environmental Context: The surrounding environment can affect how amino acids behave in terms of polarity.
What Are Examples of Polar Amino Acids?
Some common polar amino acids include:
- Serine (Ser): Contains a hydroxyl group, allowing it to participate in hydrogen bonding.
- Threonine (Thr): Similar to serine, it has a hydroxyl group that enhances its polarity.
- Asparagine (Asn): Contains an amide group, contributing to its polar properties.
- Glutamine (Gln): Also has an amide group, making it polar.
What Are Examples of Nonpolar Amino Acids?
Examples of nonpolar amino acids include:
- Glycine (Gly): The simplest amino acid with a hydrogen side chain, making it nonpolar.
- Alanine (Ala): Has a methyl group as its side chain, which is hydrophobic.
- Leucine (Leu): Contains a branched-chain alkyl side chain, making it nonpolar.
- Phenylalanine (Phe): Has a phenyl group, contributing to its nonpolar characteristics.
Are Polar Amino Acids Important for Function?
Yes, polar amino acids play a critical role in the function of proteins. Their ability to form hydrogen bonds and interact with water molecules allows proteins to maintain their structure and function in aqueous environments. Polar amino acids are often found on the surface of proteins, where they can engage in interactions with other molecules, such as substrates or signaling molecules.
How Does Polarity Affect Protein Folding?
Polarity is a significant factor in protein folding, as it influences how amino acids interact with one another and with the surrounding environment. Polar amino acids tend to be located on the exterior of proteins, where they can interact with the aqueous environment, while nonpolar amino acids are often buried in the protein's interior, away from water. This arrangement is crucial for the stability and functionality of proteins.
Can Amino Acids Change Polarity in Different Environments?
Yes, the polarity of amino acids can be influenced by their environment. Changes in pH, ionic strength, or solvent composition can affect the ionization state of amino acids, thereby altering their polarity. For instance, a polar amino acid might become less polar in a nonpolar environment, affecting how it interacts with other molecules.
Conclusion: Are Amino Acids Polar?
In summary, the question of whether amino acids are polar can be answered with a definitive yes and no. While some amino acids possess polar characteristics due to their side chains, others are nonpolar and hydrophobic. Understanding the polarity of amino acids is crucial for comprehending their functions in biological systems, including protein structure, folding, and interactions. As researchers continue to explore the complexities of amino acids, the significance of polarity remains a central theme in the study of biochemistry and molecular biology.
Discovering The Enigma Of Britannia Cait
Discovering The Vibrant World Of Filipino Entertainment
Zoechip Online: Unlocking The World Of Digital Entertainment