Circulatory systems play a vital role in the sustenance of life, serving as the body's transportation network for nutrients, gases, hormones, and waste products. These systems can be broadly categorized into two main types: open and closed circulatory systems. Understanding the intricacies of these systems not only highlights the evolutionary adaptations of various organisms but also underscores the complexity of life itself. This article will delve into the fundamental differences, advantages, and disadvantages of open and closed circulatory systems.
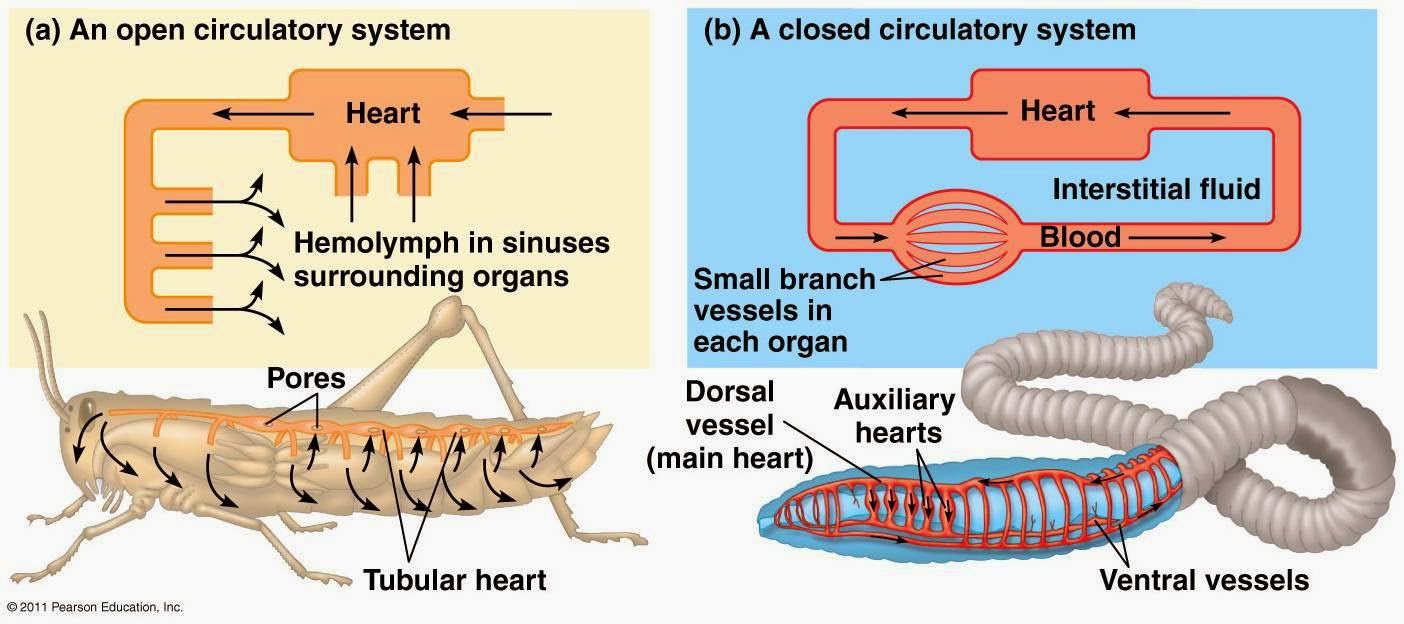
Open and closed circulatory systems are crucial to the survival of many species, including invertebrates and vertebrates. An open circulatory system, typically found in arthropods and many mollusks, allows hemolymph (a fluid analogous to blood) to flow freely through cavities and tissues. In contrast, a closed circulatory system, as seen in annelids, fish, and mammals, contains blood that circulates within a network of vessels, providing a more efficient means of transportation. By examining these two systems, we can gain insights into how different organisms have adapted to their environments.
As we journey through the realms of biology, we will uncover the underlying mechanisms that differentiate open and closed circulatory systems. What are their unique features? How do they function, and what advantages do they offer to the organisms that possess them? Join us as we explore these questions and more, revealing the extraordinary ways in which life has evolved to thrive on our planet.
What is an Open Circulatory System?
An open circulatory system is characterized by the absence of a complete network of blood vessels. Instead, the blood-like fluid, known as hemolymph, bathes the organs directly in a body cavity called the hemocoel. This system is primarily found in invertebrates, such as insects, arachnids, and crustaceans. The hemolymph is propelled by the contraction of a muscular heart, which pumps the fluid into the hemocoel, where it can exchange nutrients and gases with the surrounding tissues. The key features of an open circulatory system include:
- Low pressure: The hemolymph circulates at a lower pressure compared to closed systems.
- Less efficient nutrient delivery: The direct interaction with tissues can lead to slower nutrient transport.
- Simple structure: The absence of complex vessels simplifies the system.
What is a Closed Circulatory System?
A closed circulatory system, on the other hand, consists of a network of blood vessels that circulate blood throughout the body. This system is found in higher organisms, including all vertebrates and some invertebrates. In a closed system, the blood remains contained within vessels, allowing for more efficient transport of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products. The main characteristics of a closed circulatory system are:
- High pressure: Blood is pumped through vessels under higher pressure, allowing for faster circulation.
- Efficient nutrient delivery: The closed system enables precise control over blood flow to different organs.
- Complex structure: The presence of arteries, veins, and capillaries allows for specialization.
What Are the Advantages of Open Circulatory Systems?
Open circulatory systems offer several advantages, particularly for smaller organisms:
- Simplicity: The lack of complex vessels makes it easier for smaller organisms to manage their circulatory needs.
- Energy-efficient: The lower pressure system requires less energy to maintain.
- Adaptability: Open systems can efficiently deliver nutrients to various tissues during low activity levels.
What Are the Disadvantages of Open Circulatory Systems?
Despite their advantages, open circulatory systems also come with certain drawbacks:
- Less efficient oxygen transport: The lower pressure limits the flow of oxygen-rich hemolymph.
- Vulnerability: The exposure of hemolymph to the external environment can lead to contamination.
- Slower healing: The direct exposure to pathogens may hinder the immune response.
What Are the Advantages of Closed Circulatory Systems?
Closed circulatory systems provide several benefits, particularly for larger and more active organisms:
- Efficient oxygen transport: High pressure allows for rapid delivery of oxygen to tissues.
- Rapid healing: The contained blood can quickly respond to injuries and infections.
- Specialized circulation: Different organs can receive tailored blood flow based on their needs.
What Are the Disadvantages of Closed Circulatory Systems?
While closed circulatory systems are generally more efficient, they also have some challenges:
- Higher energy requirements: The system demands more energy to maintain blood pressure.
- Complexity: The intricate network of vessels can be prone to complications, such as blockages.
- Potential for disease: Closed systems can harbor pathogens within the bloodstream.
How Do Open and Closed Circulatory Systems Compare?
When comparing open and closed circulatory systems, it's essential to consider several factors:
- Efficiency: Closed systems offer more efficient nutrient and gas transport, especially in larger organisms.
- Pressure: Open systems operate at lower pressures, while closed systems maintain higher pressures for rapid circulation.
- Complexity: Closed systems are more complex, featuring an extensive network of vessels, while open systems are simpler.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Circulatory Systems
Open and closed circulatory systems are fascinating examples of evolutionary adaptation, showcasing the various ways organisms have evolved to meet their physiological needs. Understanding these systems offers valuable insights into biology, ecology, and the interconnectedness of life on Earth. By appreciating the unique features and functions of open and closed circulatory systems, we can better comprehend the remarkable diversity of life and the intricate processes that support it.
```
Exploring The Beginnings Of Sandra Cisneros' Writing Journey
Discovering The Beauty And Functionality Of Versalock Walls
Unlocking The Gateway: A Comprehensive Guide To Gmail Login