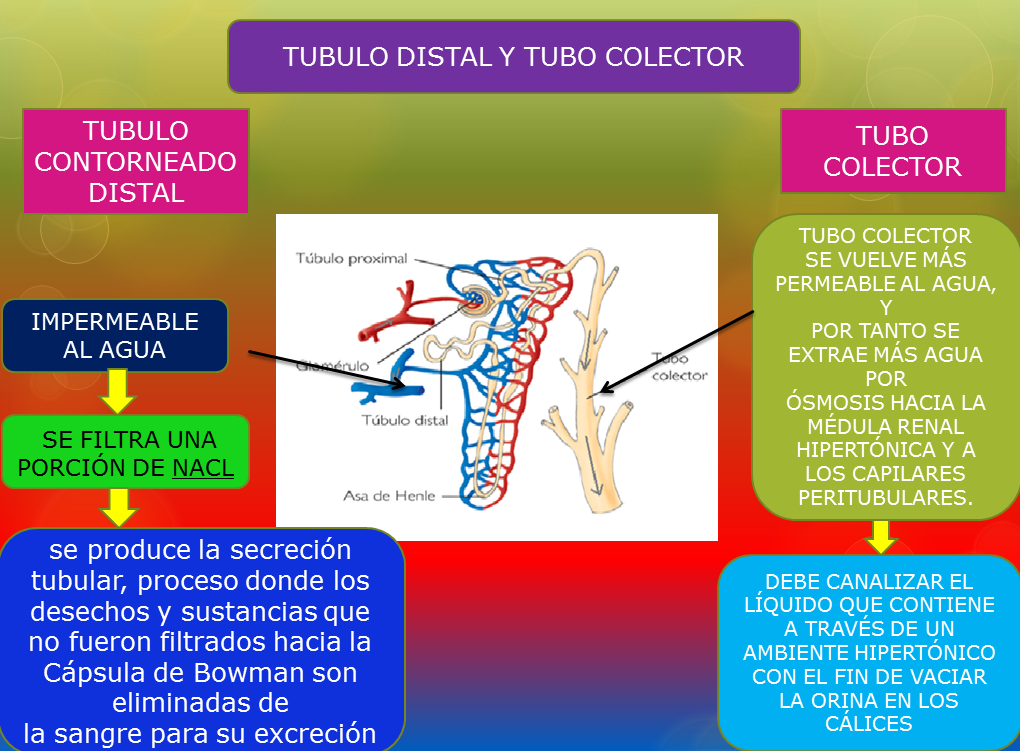
The tubulo colector is an essential structure in the nephron, playing a crucial role in the body’s ability to regulate water and electrolyte balance. This part of the kidney not only helps in the final adjustments of urine composition but also significantly contributes to maintaining homeostasis. Understanding the tubulo colector and its functions can shed light on various physiological processes and the implications of renal diseases.
As we delve deeper into the anatomy and physiology of the tubulo colector, it becomes clear that it serves as a vital conduit for transporting and modifying the filtrate that ultimately becomes urine. By exploring its intricate workings, we can appreciate how the tubulo colector impacts overall health and the consequences that arise from its dysfunction.
In this article, we will explore the tubulo colector from various angles, including its structure, function, and clinical significance. By answering key questions about this remarkable renal component, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview that will benefit both students and professionals in the field of medicine and biology.
What is the Structure of the Tubulo Colector?
The tubulo colector, also known as the collecting duct, is a series of tubules located in the kidney. It comprises a collection of nephrons, each consisting of multiple segments that work in coordination to process the filtrate. The structure of the tubulo colector can be divided into distinct regions:
- Medullary collecting ducts
- Cortical collecting ducts
- Principal cells
- Intercalated cells
These regions contribute to the tubulo colector's ability to concentrate urine and regulate the balance of electrolytes and acids.
How Does the Tubulo Colector Function?
The primary function of the tubulo colector is to collect urine from the nephrons and facilitate its final modification before excretion. This process involves several key functions:
- Reabsorption of water and solutes
- Regulation of potassium and hydrogen ion secretion
- Maintenance of acid-base balance
Through the action of hormones such as antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and aldosterone, the tubulo colector adjusts the permeability of its walls, allowing for the fine-tuning of urine composition based on the body's needs.
What Role Does Hormonal Regulation Play in the Tubulo Colector?
Hormones play a pivotal role in regulating the functions of the tubulo colector. Here are some key hormones involved:
- Antidiuretic hormone (ADH): Increases water reabsorption in the collecting ducts.
- Aldosterone: Enhances sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion.
- Parathyroid hormone (PTH): Regulates calcium reabsorption.
These hormones ensure that the tubulo colector effectively responds to varying physiological demands, ultimately maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance.
What Impact Does the Tubulo Colector Have on Kidney Health?
The health of the tubulo colector is essential for the overall function of the kidneys. Dysfunction in this area can lead to various health issues, including:
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Acid-base disorders
- Chronic kidney disease
Understanding the implications of tubulo colector dysfunction is vital for diagnosing and treating renal conditions.
Can Tubulo Colector Dysfunction Be Diagnosed?
Diagnosing tubulo colector dysfunction typically involves a combination of clinical assessments, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Common diagnostic tools include:
- Urinalysis
- Blood tests for electrolytes and kidney function
- Ultrasound or CT scans of the kidneys
These methods help healthcare providers determine the underlying causes of renal dysfunction and formulate appropriate treatment plans.
What Are the Treatment Options for Tubulo Colector Disorders?
Treatment for disorders of the tubulo colector depends on the specific condition and its severity. Possible interventions include:
- Medication to correct electrolyte imbalances
- Hormonal therapy for hormone-related dysfunctions
- Dialysis for severe kidney failure
Timely and appropriate intervention can significantly improve outcomes for patients with tubulo colector-related issues.
What Are the Future Research Directions on Tubulo Colector?
Research into the tubulo colector continues to evolve, with several promising areas of investigation, including:
- Understanding the genetic basis of tubulo colector diseases
- Developing new therapeutic approaches for renal disorders
- Exploring the role of the tubulo colector in systemic diseases
These research avenues hold the potential to enhance our understanding of kidney function and improve treatment options for patients.
Conclusion: The Importance of the Tubulo Colector in Renal Physiology
In conclusion, the tubulo colector is a critical component of the renal system that plays a vital role in maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance. Its intricate structure and hormonal regulation allow for precise adjustments to urine composition, underscoring its importance in overall health. Further research into the tubulo colector will undoubtedly lead to new insights and advancements in the diagnosis and treatment of kidney-related disorders.
Discovering The Culinary World: What Channel Is The Cooking Channel On Xfinity?
Unveiling The Extraordinary Journey Of Berniece Baker Miracle
The Vibrant Palette: Colors Of The Days Of The Week