Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, playing a crucial role in various biological processes. Their unique chemical properties determine how they interact with one another and their environment, especially in terms of polarity. Polarity refers to the distribution of electrical charge around atoms or molecules, which influences solubility, reactivity, and overall behavior in biological systems. In this article, we will delve into the question: are amino acids polar? Understanding the polarity of these essential molecules can provide insights into their functions and interactions within living organisms.
In biochemistry, amino acids are categorized based on their side chains, which can either be polar or nonpolar. This classification affects how they interact with water and other molecules. Polar amino acids generally have side chains that can form hydrogen bonds with water, making them hydrophilic, while nonpolar amino acids are hydrophobic and tend to avoid water. This distinction is crucial in protein folding, as it influences the tertiary structure of proteins and their functionality.
As we explore the question of polarity in amino acids, it is essential to consider factors such as the role of functional groups, the environment in which amino acids are found, and their interactions with other biomolecules. This article aims to provide comprehensive information on the polarity of amino acids, their classifications, and their implications in biochemical processes.
What are Amino Acids?
Amino acids are organic compounds that serve as the building blocks of proteins. There are 20 standard amino acids, each with a specific structure and function. They consist of a central carbon atom, an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a variable side chain (R group). The side chain differentiates one amino acid from another and determines its characteristics, including polarity.
Are Amino Acids Polar or Nonpolar?
The polarity of amino acids is primarily determined by their side chains. Amino acids can be classified into three categories based on their polarity:
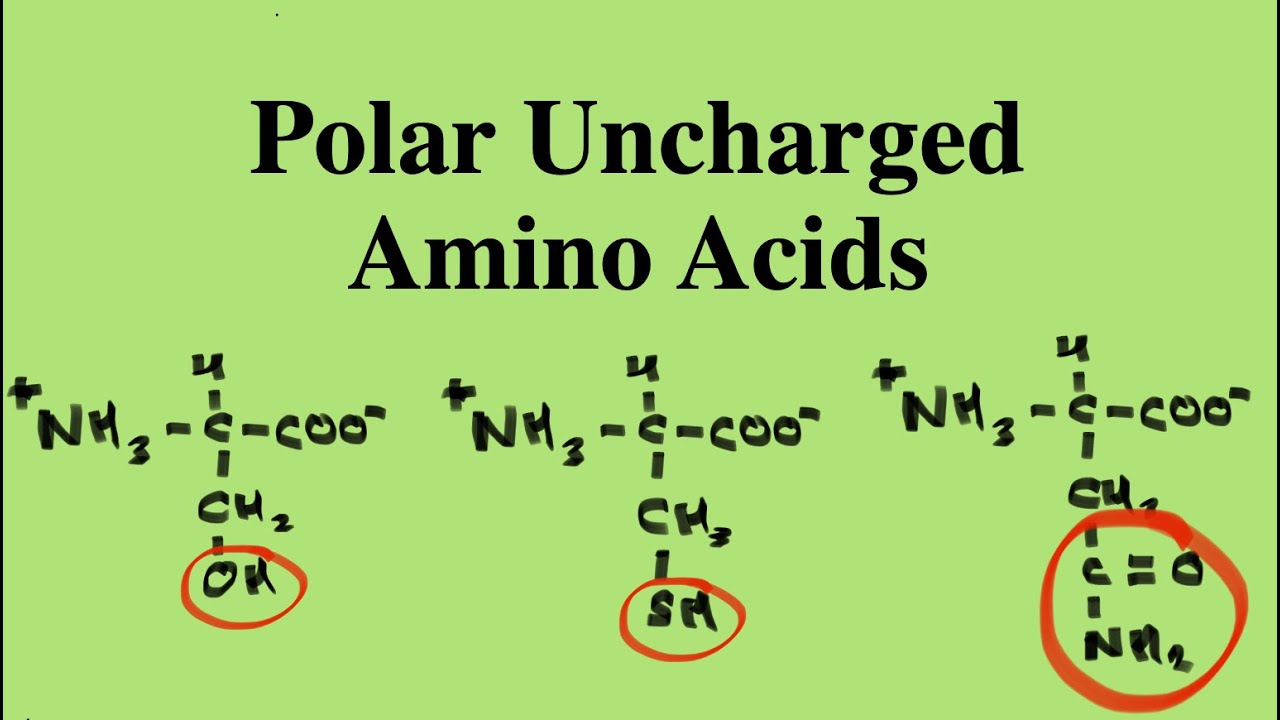
- Polar Amino Acids: These amino acids have side chains that are hydrophilic and can interact with water. Examples include serine, threonine, and asparagine.
- Nonpolar Amino Acids: These amino acids have hydrophobic side chains that do not interact well with water. Examples include leucine, isoleucine, and valine.
- Charged Amino Acids: These amino acids possess a charge on their side chains, making them highly polar. Examples include lysine, arginine, and glutamic acid.
How Does the Polarity of Amino Acids Affect Protein Structure?
The polarity of amino acids significantly influences protein folding and stability. In aqueous environments, polar amino acids tend to be found on the exterior of proteins, interacting with the surrounding water molecules. In contrast, nonpolar amino acids are usually buried within the protein structure, away from water. This arrangement is crucial for the formation of the protein's three-dimensional shape, which ultimately determines its function.
Which Amino Acids are Considered Polar?
Polar amino acids are characterized by their ability to form hydrogen bonds due to the presence of electronegative atoms, such as nitrogen or oxygen, in their side chains. Here are some examples of polar amino acids:
- Serine (Ser)
- Threonine (Thr)
- Asparagine (Asn)
- Glutamine (Gln)
- Cysteine (Cys)
Are Amino Acids Polar in Different Environments?
The polarity of amino acids can be influenced by their surrounding environment. In polar solvents like water, polar amino acids are more soluble and readily interact with other molecules. Conversely, in nonpolar solvents, the behavior of amino acids may differ, and their interactions can lead to changes in protein structure and function.
Why is Understanding Amino Acid Polarity Important?
Understanding whether amino acids are polar is crucial for several reasons:
- Protein Design: Knowledge of amino acid polarity aids in the design of proteins for various applications, including enzyme engineering and drug development.
- Biological Function: The polarity of amino acids affects protein folding, stability, and interactions, which are essential for biological function.
- Research Implications: Understanding polarity helps researchers predict how proteins will behave under different conditions, which is valuable in fields like biochemistry and molecular biology.
How Do Polar and Nonpolar Amino Acids Interact?
Polar and nonpolar amino acids interact differently within protein structures. Polar amino acids can form hydrogen bonds with each other and with water, while nonpolar amino acids tend to aggregate together, avoiding contact with water. This interaction leads to the formation of hydrophobic cores within proteins, which contribute to their stability and functionality.
Conclusion: Are Amino Acids Polar?
In conclusion, the polarity of amino acids is a fundamental aspect of their chemistry and biology. Understanding whether amino acids are polar or nonpolar not only provides insights into protein structure and function but also has implications for various scientific fields. By recognizing the importance of amino acid polarity, researchers and biochemists can better understand the complex interactions that govern life at the molecular level.
Aphmau's All Videos New: A Dive Into The Vibrant World Of A YouTube Sensation
Unlocking Opportunities: The Benefits Of Global Sourcing
Mastering The Art Of Merging: How To Merge Master Into Branch In GitHub