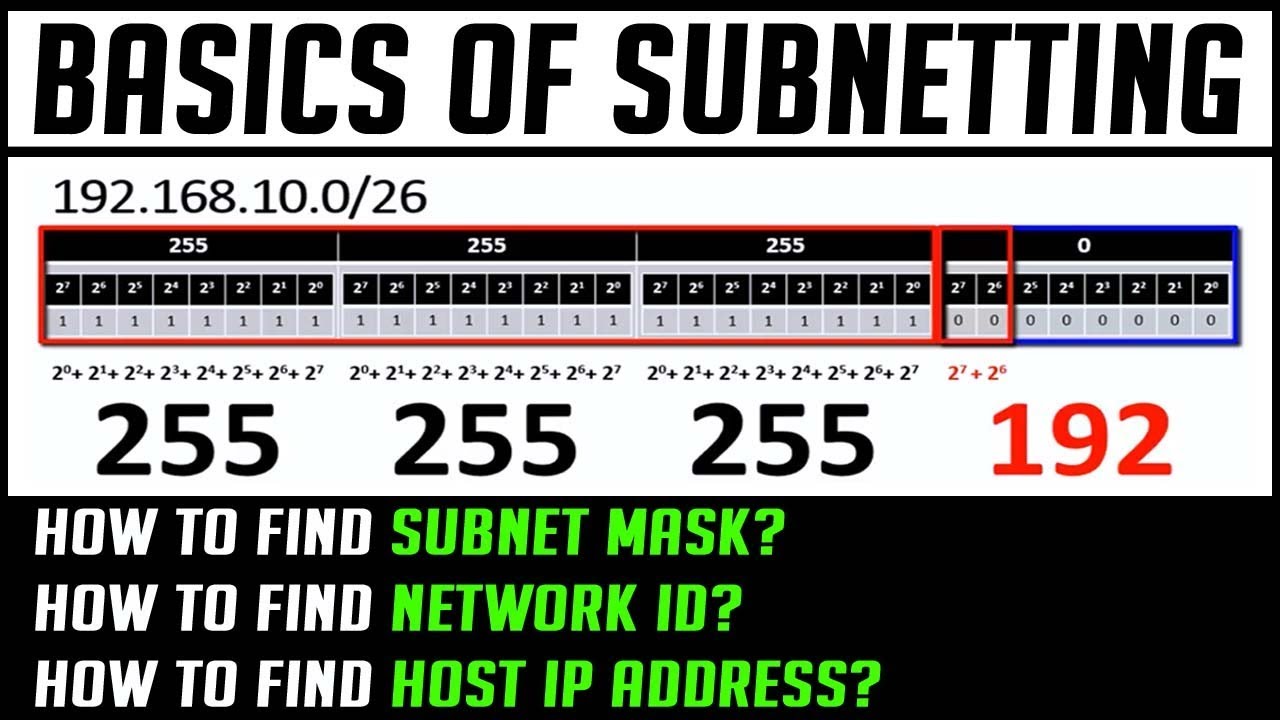
In the ever-evolving world of networking, understanding how to calculate the subnet mask is crucial for effective and efficient network management. The subnet mask is a fundamental concept that allows network administrators to divide a single network into smaller, manageable segments, known as subnets. This division not only enhances security but also optimizes performance by reducing congestion. A clear grasp of subnetting is essential for anyone looking to succeed in the field of IT and network administration.
For beginners, the concept of subnetting and subnet masks may seem daunting. However, with the right approach and a little practice, calculating the subnet mask can become second nature. This article will break down the process into manageable steps, making it easier to understand how to calculate the subnet mask and apply it in real-world scenarios. By the end of this guide, you will gain confidence in your ability to work with subnet masks and subnetting.
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of subnet masks, we will cover various aspects, including the binary representation, CIDR notation, and common subnetting practices. Whether you're a seasoned network engineer or just starting your journey in networking, our guide on how to calculate the subnet mask will provide valuable insights and practical knowledge.
What is a Subnet Mask?
A subnet mask is a 32-bit number used in conjunction with an IP address to determine which portion of the address identifies the network and which part identifies the host. It is typically expressed in the same format as an IP address, consisting of four octets, such as 255.255.255.0. Understanding subnet masks is fundamental for creating and managing networks effectively.
How Does a Subnet Mask Work?
The subnet mask operates by using a series of binary digits (0s and 1s) to define the network and host portions of an IP address. In a subnet mask, a "1" bit represents the network portion, while a "0" bit represents the host portion. By applying a subnet mask to an IP address, devices can determine whether two IP addresses belong to the same network or if they need to be routed through a gateway.
Why is Subnetting Important?
- Improved Network Performance: Subnetting reduces broadcast traffic by limiting the size of each subnet.
- Enhanced Security: Different subnets can have different security policies, protecting sensitive data.
- Efficient IP Address Management: Subnetting allows for better utilization of IP address space.
- Organizational Structure: Subnets can represent different departments or locations within an organization.
How to Calculate the Subnet Mask?
Calculating the subnet mask involves understanding the binary representation of IP addresses and how to manipulate them. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to calculate the subnet mask:
- Identify the IP Address and CIDR Notation: Determine the IP address and its CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) notation. For example, 192.168.1.0/24.
- Convert CIDR to Subnet Mask: The CIDR notation indicates how many bits are used for the network portion. For /24, the subnet mask in binary is 11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000, which equals 255.255.255.0.
- Write the Subnet Mask in Decimal: Convert the binary representation into decimal format, resulting in 255.255.255.0.
- Verify the Calculation: Ensure that the subnet mask corresponds to the correct number of hosts and networks required for your design.
What is CIDR Notation and How is it Used?
CIDR notation is a shorthand method of representing the subnet mask alongside the IP address. It simplifies the representation by indicating the number of bits allocated for the network portion. For example, in the IP address 192.168.1.0/24, the "/24" signifies that the first 24 bits are for the network, leaving the remaining 8 bits for host addresses. This notation is widely used in modern networking due to its efficiency and ease of understanding.
What are Common Subnet Masks?
Here are some common subnet masks and their corresponding CIDR notations:
| Subnet Mask | CIDR Notation | Number of Hosts |
|---|---|---|
| 255.0.0.0 | /8 | 16,777,214 |
| 255.255.0.0 | /16 | 65,534 |
| 255.255.255.0 | /24 | 254 |
| 255.255.255.255 | /32 | 1 |
How to Calculate Subnet Masks for Different Networks?
When working with different network designs, it’s essential to calculate subnet masks based on specific requirements, such as the number of hosts needed. Follow these steps:
- Determine the Number of Required Hosts: Calculate the number of devices that will connect to the network.
- Use the Formula: Use the formula 2^n - 2 ≥ Number of Hosts, where n is the number of host bits. Solve for n to find the necessary number of bits.
- Calculate the Subnet Mask: Subtract the number of host bits from 32 to find the number of network bits. Convert this to CIDR notation.
What Tools Can Help in Subnet Mask Calculation?
There are various online tools and calculators available that can simplify the process of calculating subnet masks. Some popular options include:
- Subnet calculators
- IP address management tools
- Networking software with built-in subnetting features
Conclusion: Mastering Subnetting for Network Efficiency
Understanding how to calculate the subnet mask is a vital skill for anyone involved in networking. By mastering this concept, you can enhance network performance, improve security, and effectively manage IP address allocation. With practice, the process of calculating subnet masks will become intuitive, allowing you to design efficient networks that meet the unique needs of your organization.
Understanding Body Dysphoria: A Comprehensive Guide To The Body Dysphoria Test
Everything You Need To Know About Canceling Your Costco Membership
Understanding The Cost Of Drywall: A Comprehensive Guide