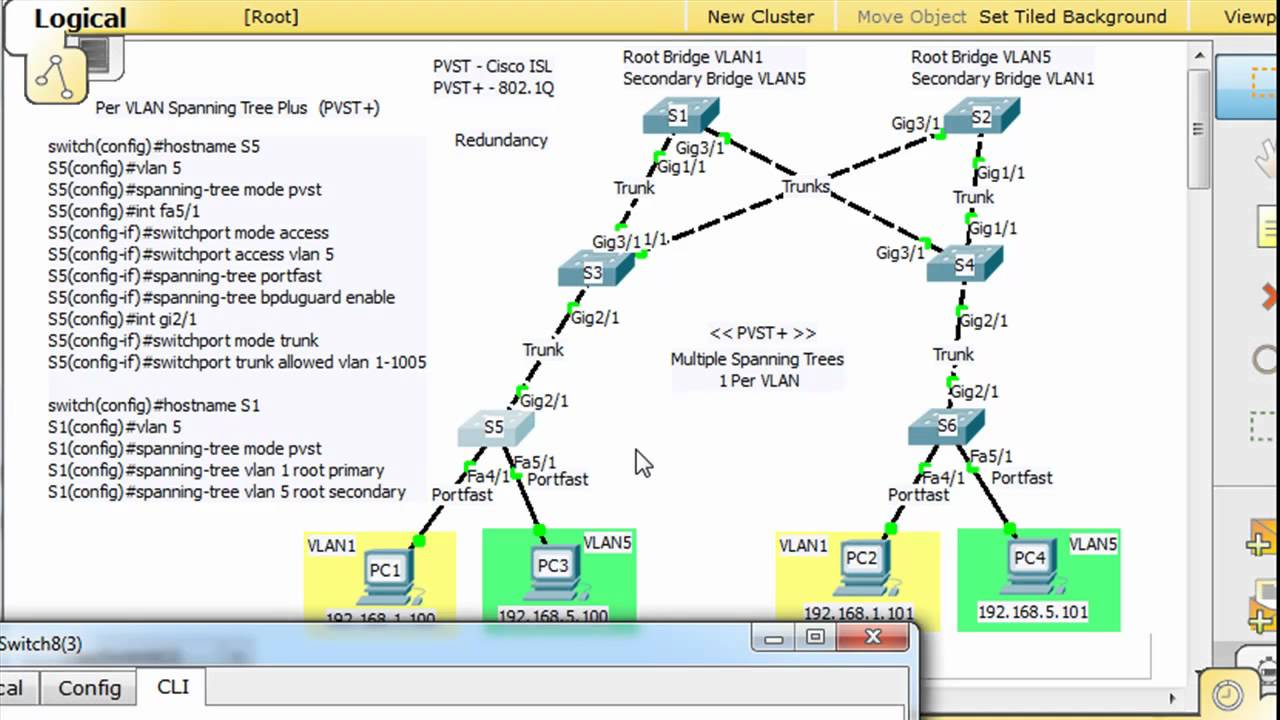
In the world of networking, ensuring efficient data flow while maintaining redundancy is paramount. One of the cornerstone protocols that help achieve this is the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), and its variant, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST). PVST is essential for managing VLANs in a network, allowing for loop-free topologies and optimal path selection. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of spanning-tree mode PVST, including its functionality, advantages, and practical applications within networking environments.
The Spanning Tree Protocol was developed to prevent loops in Ethernet networks. With the advent of Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs), there arose a need for a more efficient version of STP that could cater to each VLAN independently. This is where PVST comes into play, allowing each VLAN to maintain its own spanning tree. As we explore the spanning-tree mode PVST, we will discuss how it operates, its configuration, and the benefits it provides to network administrators who seek to optimize their networks while ensuring redundancy.
By incorporating spanning-tree mode PVST into your network infrastructure, you can significantly enhance performance and reliability. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of PVST, addressing common questions and clarifying its essential features. Whether you're a seasoned network engineer or a newcomer to the field, understanding spanning-tree mode PVST is crucial for maintaining an efficient and resilient network.
What is Spanning-Tree Mode PVST?
Spanning-tree mode PVST, or Per-VLAN Spanning Tree, is a networking protocol that allows for the creation of separate spanning trees for each VLAN within a network. This means that each VLAN can have its own root bridge and topology, which helps to prevent loops and ensures that data flows efficiently across the network.
How Does Spanning-Tree Mode PVST Operate?
The operation of spanning-tree mode PVST involves several key steps:
- Bridge Election: Each switch in the network participates in a bridge election process to determine the root bridge for each VLAN.
- Path Cost Calculation: The switches calculate the path cost to the root bridge, determining the best path for data transmission.
- Port Roles Assignment: Ports on the switches are assigned roles based on their position in the topology, including root port, designated port, and blocked port.
- Topology Maintenance: The spanning-tree topology is maintained through the exchange of Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) among switches.
What Are the Benefits of Using Spanning-Tree Mode PVST?
Implementing spanning-tree mode PVST in your networking environment offers several advantages:
- Loop Prevention: PVST effectively prevents loops that can cause broadcast storms, ensuring smooth data transmission.
- Load Balancing: With separate spanning trees for each VLAN, traffic can be distributed more evenly across the network.
- Improved Redundancy: In the event of a link failure, PVST quickly recalculates the topology, allowing for rapid recovery and minimal downtime.
- Scalability: PVST is designed to scale efficiently with the addition of new VLANs, making it suitable for growing networks.
How to Configure Spanning-Tree Mode PVST?
Configuring spanning-tree mode PVST on Cisco devices is straightforward. Here are the basic steps:
- Access the device's command line interface (CLI).
- Enter global configuration mode.
- Enable spanning-tree mode PVST:
- Configure the VLANs as needed:
- Assign ports to the VLANs:
- Save the configuration:
spanning-tree mode pvst
vlanname exit
interfaceswitchport mode access switchport access vlan exit
write memory
What Challenges Might You Face with Spanning-Tree Mode PVST?
While spanning-tree mode PVST has many benefits, there are also challenges to consider:
- Increased CPU Utilization: Each VLAN has its own spanning tree, which can lead to higher CPU usage on switches.
- Complexity: Managing multiple spanning trees can make network configuration and troubleshooting more complex.
- Convergence Time: Although PVST provides quick convergence, it may still be slower compared to Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP).
Is There an Alternative to Spanning-Tree Mode PVST?
Yes, there are alternatives to spanning-tree mode PVST that may be more suitable for certain network environments:
- Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP): Offers faster convergence times and is suitable for modern networks.
- Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP): Allows multiple VLANs to share a single spanning tree, reducing complexity and CPU usage.
Conclusion: Why Choose Spanning-Tree Mode PVST?
In conclusion, spanning-tree mode PVST is a robust and effective solution for managing VLANs in a network environment. It provides essential loop prevention, load balancing, and redundancy, making it an ideal choice for organizations looking to optimize their network infrastructure. While there are challenges associated with its implementation, the benefits often outweigh the drawbacks, especially in environments where VLANs play a significant role in network design. Understanding and configuring spanning-tree mode PVST will empower network administrators to maintain a reliable and efficient network.
Understanding The Past Tense Of "Leave": Examples And Usage
Discovering The Secrets Of OSRS Willow Branch
Understanding Inorganic Molecules: The Building Blocks Of Life