In the realm of networking, a subnet mask table serves as a crucial tool for managing and organizing IP addresses within a network. It plays an integral role in determining how data packets are forwarded to their destinations, ensuring efficient communication between devices. By breaking down IP networks into smaller, manageable sub-networks, the subnet mask table enhances network security and performance, allowing for streamlined data transmission.
As organizations grow and the demand for efficient networking solutions increases, understanding subnetting becomes essential. A subnet mask table provides a visual reference for network administrators, enabling them to assign IP addresses strategically and avoid conflicts. Moreover, it helps in conserving IP addresses, thus playing a significant role in the sustainability of network resources.
In this article, we will explore the intricacies of the subnet mask table, answering common questions and providing valuable insights into its functionality. From understanding the fundamental concepts of subnetting to practical applications and examples, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of IP networking.
What is a Subnet Mask Table?
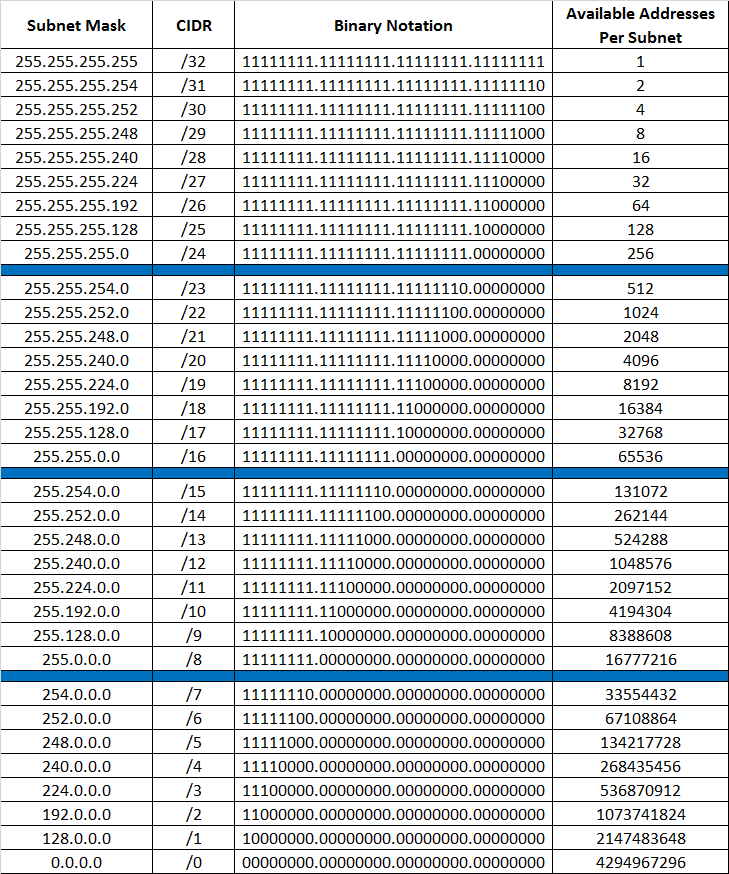
A subnet mask table is a reference chart that outlines the relationship between IP addresses and their corresponding subnet masks. It helps network administrators to determine how many hosts can be accommodated within a given subnet and how to allocate IP addresses efficiently. The table typically includes the following information:
- Subnet Mask
- CIDR Notation
- Number of Hosts
- Network Address
- Broadcast Address
Why is a Subnet Mask Important?
The subnet mask is essential for directing network traffic and ensuring that data packets reach their intended destinations. By defining the network portion and the host portion of an IP address, the subnet mask enables routers and switches to make informed decisions about data forwarding. Without proper subnetting, networks can become congested, leading to poor performance and increased latency.
How Does Subnetting Work?
Subnetting involves dividing a larger network into smaller subnetworks, or subnets. Each subnet operates independently, allowing for efficient management of IP addresses. The subnet mask table aids in this process by providing a structured approach to subnetting, which includes:
- Identifying the network address
- Determining the subnet mask
- Calculating the number of hosts
- Assigning IP addresses
What are the Components of a Subnet Mask Table?
The subnet mask table comprises several key components that are crucial for understanding how subnetting operates. Here are the main elements:
- Subnet Mask: A 32-bit value that separates the network and host portions of an IP address.
- CIDR Notation: A shorthand representation of the subnet mask, indicating the number of bits used for the network portion.
- Number of Hosts: The total number of usable IP addresses within a subnet.
- Network Address: The first address in a subnet, used to identify the subnet as a whole.
- Broadcast Address: The last address in a subnet, used to communicate with all devices within that subnet.
How to Create a Subnet Mask Table?
Creating a subnet mask table requires a systematic approach. Here are the steps to generate your own subnet mask table:
- Determine the size of your network and the number of subnets needed.
- Select a base IP address for your network.
- Choose an appropriate subnet mask based on the desired number of hosts per subnet.
- Calculate the CIDR notation for the subnet mask.
- Fill in the subnet mask table with the relevant information, including the network and broadcast addresses.
What are Common Subnet Masks?
Here are some commonly used subnet masks and their corresponding CIDR notations:
| Subnet Mask | CIDR Notation | Number of Hosts |
|---|---|---|
| 255.0.0.0 | /8 | 16,777,214 |
| 255.255.0.0 | /16 | 65,534 |
| 255.255.255.0 | /24 | 254 |
| 255.255.255.192 | /26 | 62 |
| 255.255.255.224 | /27 | 30 |
How to Read a Subnet Mask Table?
Reading a subnet mask table is straightforward once you understand the components. Each row typically represents a different subnet configuration, allowing you to compare subnet masks, CIDR notations, and the corresponding number of hosts. Here’s a brief guide on how to interpret the information:
- Identify the subnet mask to determine the size of the subnet.
- Refer to the CIDR notation for a concise representation of the mask.
- Check the number of hosts to understand the capacity of each subnet.
What are the Benefits of Using a Subnet Mask Table?
The advantages of utilizing a subnet mask table are numerous:
- Improved Network Performance: Efficiently managing IP addresses helps to reduce network congestion.
- Enhanced Security: Subnetting can isolate sensitive data and devices within specific subnets.
- Better Resource Allocation: A subnet mask table aids in maximizing the use of available IP addresses.
- Simplified Troubleshooting: Identifying network issues becomes easier with a clear understanding of subnet configurations.
Conclusion: Mastering the Subnet Mask Table
In conclusion, mastering the subnet mask table is vital for anyone involved in network management. By comprehending the fundamentals of subnetting and effectively utilizing a subnet mask table, network administrators can optimize their networks for performance, security, and resource management. As technology continues to evolve, understanding these networking principles will remain essential for staying ahead in the field.
Unleashing The Power Of Force Regeneration
Germany And The League Of Nations: An Intricate Relationship
Unlocking Connections: How To Make Your Device Discoverable